Background of Last-Mile Logistics

Last-mile delivery is a crucial component of the global e-commerce industry.
However, it faces significant challenges that require innovative solutions.
Statistics reveal that last-mile logistics accounts for 41% of the total delivery cost worldwide, which combined with outdated techniques and inefficiencies, fails to meet the growing needs of consumers.
To overcome these challenges, the industry should concentrate on enhancing user experience, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency through technology.
For companies to stay competitive, smart solutions are paramount and collaboration among consumers, logistics firms, e-commerce platforms, governments, and tech providers is necessary for building a smarter last-mile logistics ecosystem.
Embracing new technologies and solutions can help drive progress in the industry.
What is Last Mile Logistics?
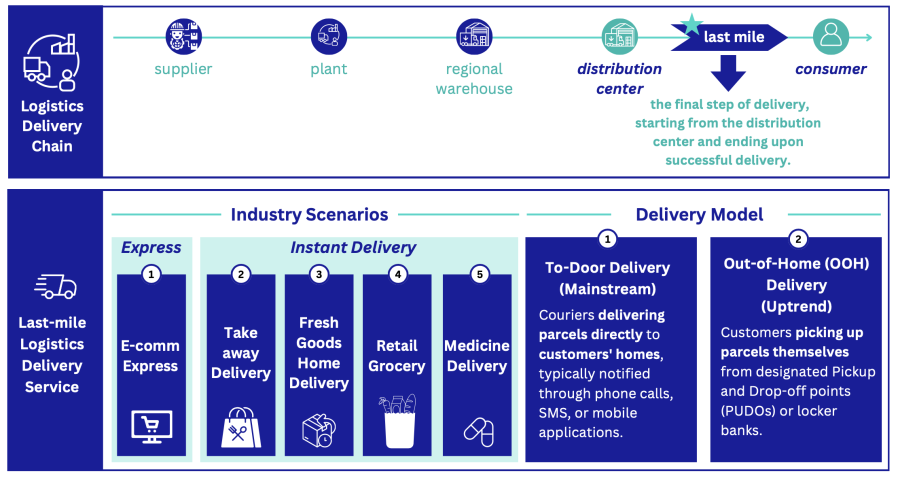
Last-mile logistics refers to the final stage of the logistics distribution process, which includes all the activities involved in delivering products from the supplier to the consumer.
This stage is crucial as it involves meeting the customers’ needs and expectations, starting from distribution centers and concluding with successful delivery to the consumer’s doorstep.
In this domain, two primary delivery models are prevalent.
1. To-Door Delivery Mode
This traditional model involves couriers delivering parcels directly to customers’ homes, typically notified through phone calls, SMS, or mobile applications.
It remains the predominant method in most countries, offering convenience to consumers.
2. Out-of-Home (OOH) Delivery Mode
OOH delivery entails customers picking up parcels themselves from designated Pickup and Drop-off points (PUDOs) or parcel lockers.
This emerging model caters to evolving consumer preferences for flexibility and convenience, especially in urban areas.
Smart Last-Mile Logistics
The imperative for smart last-mile logistics arises from many challenges and necessities.
Challenges
- The existing delivery infrastructure is strained due to the increasing demands of e-commerce and population growth, resulting in inefficiencies and rising costs.
- Additionally, environmental concerns necessitate the adoption of sustainable distribution practices to mitigate carbon emissions and reduce energy consumption.
- Furthermore, technological limitations hinder the implementation of innovative delivery solutions and impede operational efficiency.
Necessities
- As consumers’ expectations for seamless delivery experiences continue to grow, it becomes increasingly important for businesses to invest in technological advancements and operational improvements.
- Enterprises constantly seek ways to reduce costs and enhance efficiency in response to changing market dynamics and competitive pressures.
- Governments also recognize last-mile logistics’s crucial role in economic development and sustainability, leading them to initiate programs that encourage innovation and regulatory frameworks.
The 4E Model
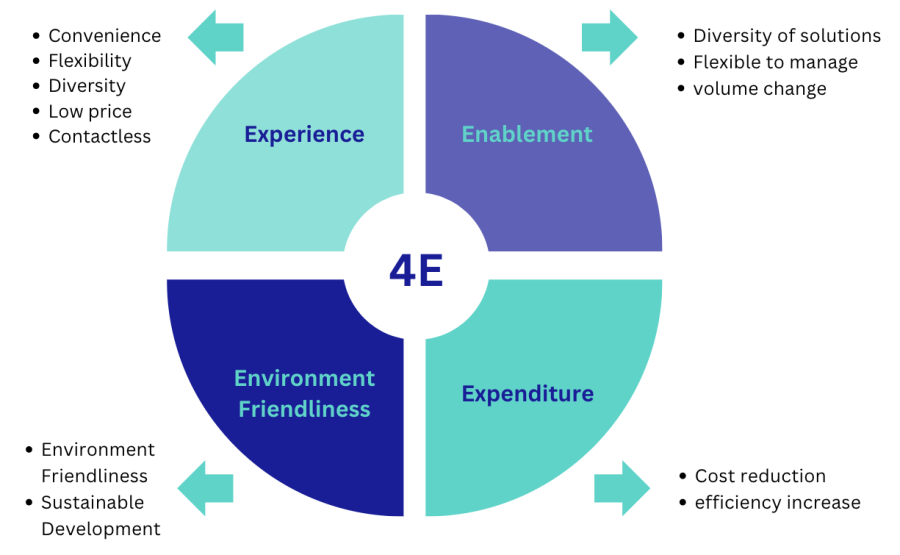
In response to these challenges and necessities, stakeholders advocate for the adoption of the 4E model:
Experience
Prioritizing user experience through enhanced punctuality, privacy, convenience, and affordability.
Enablement
Empowering enterprises with diverse solutions to manage volume fluctuations and adapt to changing consumer demands.
Environmental-Friendliness
Embracing sustainable practices to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmental conservation.
Expenditure
Optimizing costs and efficiency to alleviate financial burdens and enhance competitiveness.
Government Policies
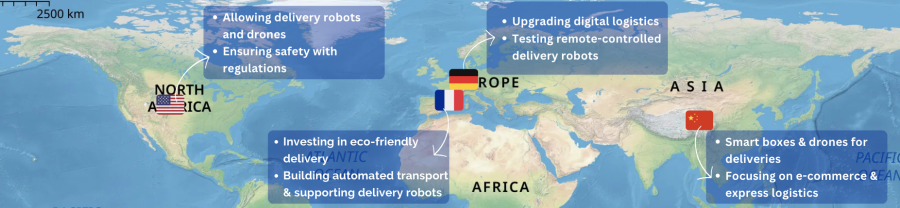
Governments worldwide are spearheading initiatives to promote innovation and sustainability in last-mile logistics, such as:
🇨🇳 China
- The government has prioritized the integration of smart technologies like smart express boxes and unmanned vehicles into last-mile delivery services.
- This initiative is part of broader policies to promote the coordinated development of e-commerce and express logistics.
🇺🇸 United States
- Various states in the U.S. have issued regulations governing the operation of unmanned delivery vehicles, encouraging the deployment of autonomous delivery robots and drones.
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has introduced regulations to ensure the safety of driverless cars, fostering innovation in autonomous delivery technologies.
🇫🇷 France
- France is investing in green and smart logistics development to reduce carbon emissions and enhance delivery efficiency.
- In 2021, the country announced plans to invest €200 million in constructing automated, low-carbon transport infrastructure.
- An additional €90 million will support “logistics 4.0” projects, focusing on enhancing facilities for innovative logistics methods like delivery robots and drones.
🇩🇪 Germany
- Germany’s Logistics 2030 Innovation Programme aims to bolster its digital logistics infrastructure.
- This initiative prioritizes scalable digital solutions and technological advancements, including remote-controlled delivery robots.
- Pilot projects are underway to integrate innovative transportation methods, ensuring adaptability and efficiency in the logistics sector.
Smart Last-Mile Logistics Solutions
Several innovative solutions have emerged to address the challenges of last-mile delivery:
1. Smart PUDO
Equipped with intelligent solutions, Pick-Up and Drop-Off (PUDO) locations offer convenience and efficiency in parcel collection.
2. Smart Locker Banks
These automated facilities provide secure parcel storage and retrieval, offering a 24/7 pick-up service to consumers.
3. Unmanned Vehicles
From small-scale drones to larger unmanned vehicles, automation promises to improve delivery capabilities and overall efficiency.
4. Drone Delivery
Drones offer the potential for rapid delivery in urban and remote areas, though safety and cost concerns remain significant hurdles.
Smart Last-Mile Logistics Ecosystem
The ecosystem of smart last-mile logistics comprises four key stakeholders:
1. End Users
Consumers drive demand for personalized and efficient delivery experiences, influencing the development of business models and technologies.
2. Regulators
Government agencies and property management entities guide and regulate the development of smart last-mile logistics through policy measures and infrastructure support.
3. Integrators
Logistics companies, e-commerce platforms, and third-party providers integrate solutions to design and operate smart last-mile logistics services.
4. Other Service Participants
Technology service enterprises and other partners contribute to developing and implementing smart last-mile logistics solutions.
Conclusion
In the world of global commerce, the efficiency of last-mile logistics is of utmost importance.
This industry is currently undergoing significant changes due to increasing demands, environmental concerns, and technological limitations.
However, the rise of smart last-mile logistics brings hope for innovation and efficiency through initiatives such as the 4E model and government policies that promote sustainability and technology integration.
Various stakeholders are driving progress in this regard.
Innovative solutions, such as smart PUDO locations and unmanned vehicles, are reshaping the landscape of this industry and promising greater efficiency and sustainability.
However, collaboration among stakeholders is the key to moving forward.
By working together, we can create a future where last-mile logistics is not just a challenge but an opportunity for sustainable growth and improved customer satisfaction.
Source: Deloitte 2023 Global Smart Last-Mile Logistics Outlook